A quantity of completely different intracellular signing pathways have been proven to be activated by receptor tyrosine kinases. These activation occasions embody the phosphoinositide 3-kinase, 70 kDa S6 kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), phospholipase C-gamma, and the Jak/STAT pathways.
The exact function of every of these pathways in cell signing stays to be resolved, however research on the differentiation of mammalian PC12 cells in tissue tradition and the genetics of cell destiny willpower in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis counsel that the extracellular sign–regulated kinase (ERK-regulated) MAPK pathway could also be enough for these mobile responses. Experiments with PC12 cells additionally counsel that the length of ERK activation is crucial for cell signing selections .
Apoptosis performs an essential function throughout neuronal growth, and defects in apoptosis could underlie varied neurodegenerative issues.
To characterize molecular mechanisms that regulate neuronal apoptosis, the contributions to cell loss of life of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase relations, together with ERK (extracellular sign–regulated kinase), JNK (c-JUN NH2-terminal protein kinase), and p38, have been examined after withdrawal of nerve progress issue (NGF) from rat PC-12 pheochromocytoma cells.

NGF withdrawal led to sustained activation of the JNK and p38 enzymes and inhibition of ERKs. The results of dominant-interfering or constitutively activated varieties of varied parts of the JNK-p38 and ERK signing pathways demonstrated that activation of JNK and p38 and concurrent inhibition of ERK are crucial for induction of apoptosis in these cells.
Therefore, the dynamic steadiness between progress factor-activated ERK and stress-activated JNK-p38 pathways could also be essential in figuring out whether or not a cell survives or undergoes apoptosis.
The RAS/RAF signing pathway is a crucial mediator of tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis. The novel bi-aryl urea BAY 43-9006 is a potent inhibitor of Raf-1, a member of the RAF/MEK/ERK signing pathway. Additional characterization confirmed that BAY 43-9006 suppresses each wild-type and V599E mutant BRAF exercise in vitro.
In addition, BAY 43-9006 demonstrated vital exercise towards a number of receptor tyrosine kinases concerned in neovascularization and tumor development, together with vascular endothelial progress issue receptor (VEGFR)-2, VEGFR-3, platelet-derived progress issue receptor beta, Flt-3, and c-KIT.
In mobile mechanistic assays, BAY 43-9006 demonstrated inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in colon, pancreatic, and breast tumor cell traces expressing mutant KRAS or wild-type or mutant BRAF, whereas non-small-cell lung most cancers cell traces expressing mutant KRAS have been insensitive to inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by BAY 43-9006.
Potent inhibition of VEGFR-2, platelet-derived progress issue receptor beta, and VEGFR-Three mobile receptor autophosphorylation was additionally noticed for BAY 43-9006.
Once day by day oral dosing of BAY 43-9006 demonstrated broad-spectrum antitumor exercise in colon, breast, and non-small-cell lung most cancers xenograft fashions. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated a detailed affiliation between inhibition of tumor progress and inhibition of the extracellular sign–regulated kinases (ERKs) half of phosphorylation in two of three xenograft fashions examined, in line with inhibition of the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway in some however not all fashions.
Additional analyses of microvessel density and microvessel space in the identical tumor sections utilizing antimurine CD31 antibodies demonstrated vital inhibition of neovascularization in all three of the xenograft fashions. These knowledge display that BAY 43-9006 is a novel twin motion RAF kinase and VEGFR inhibitor that targets tumor cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis.
Multicellular organisms have three well-characterized subfamilies of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) that management an unlimited array of physiological processes. These enzymes are regulated by a attribute phosphorelay system by which a sequence of three protein kinases phosphorylate and activate each other. The extracellular sign–regulated kinases (ERKs) perform within the management of cell division, and inhibitors of these enzymes are being explored as anticancer brokers.
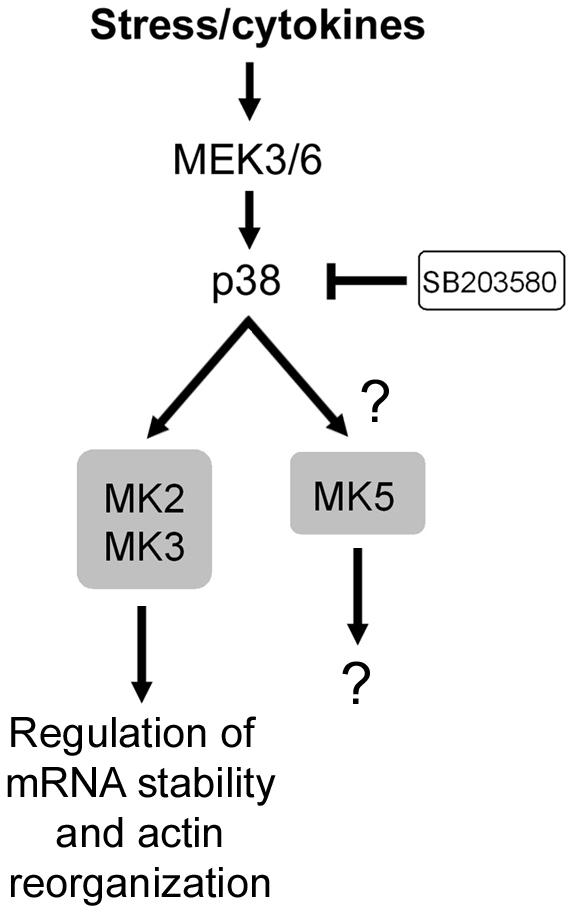
The c-Jun amino-terminal kinases (JNKs) are crucial regulators of transcription, and JNK inhibitors could also be efficient in management of rheumatoid arthritis. The p38 MAPKs are activated by inflammatory cytokines and environmental stresses and will contribute to ailments like bronchial asthma and autoimmunity.